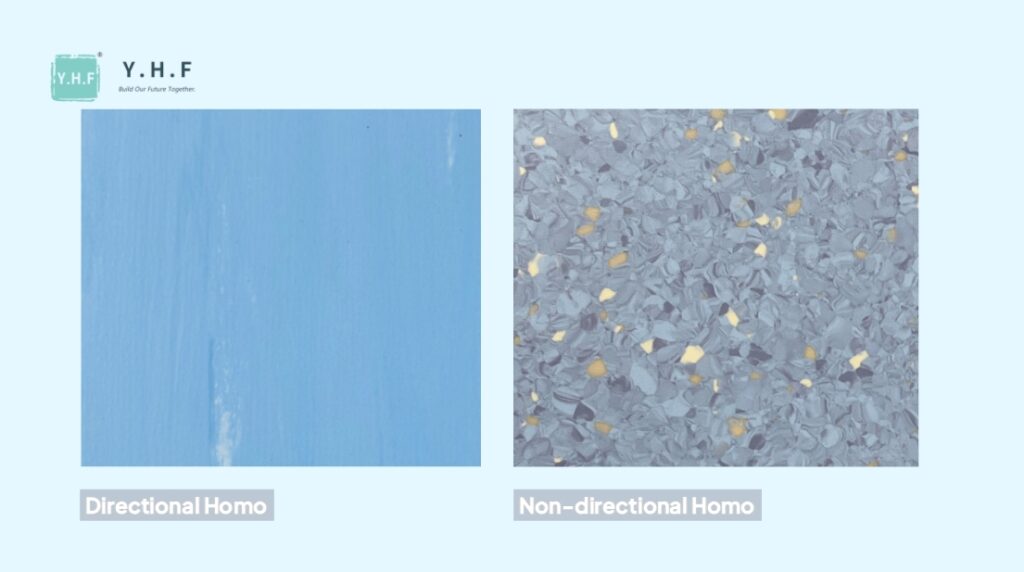
Homogeneous vinyl flooring is a single-layer, through-colored sheet flooring, typically sized 2m x 2m. Its color and pattern run through the entire thickness, meaning scratches or wear do not affect its appearance.
This flooring is generally classified into two types: Directional and Non-Directional.
1. Pattern & Installation
Non-directional: Features a random, terrazzo-like or gravel pattern with no directional grain. Installation is more flexible, and seams are less noticeable—no alignment required.
Directional: Displays distinct directional patterns, such as linear stripes. Installation must follow the same direction to avoid visible color or pattern mismatches.
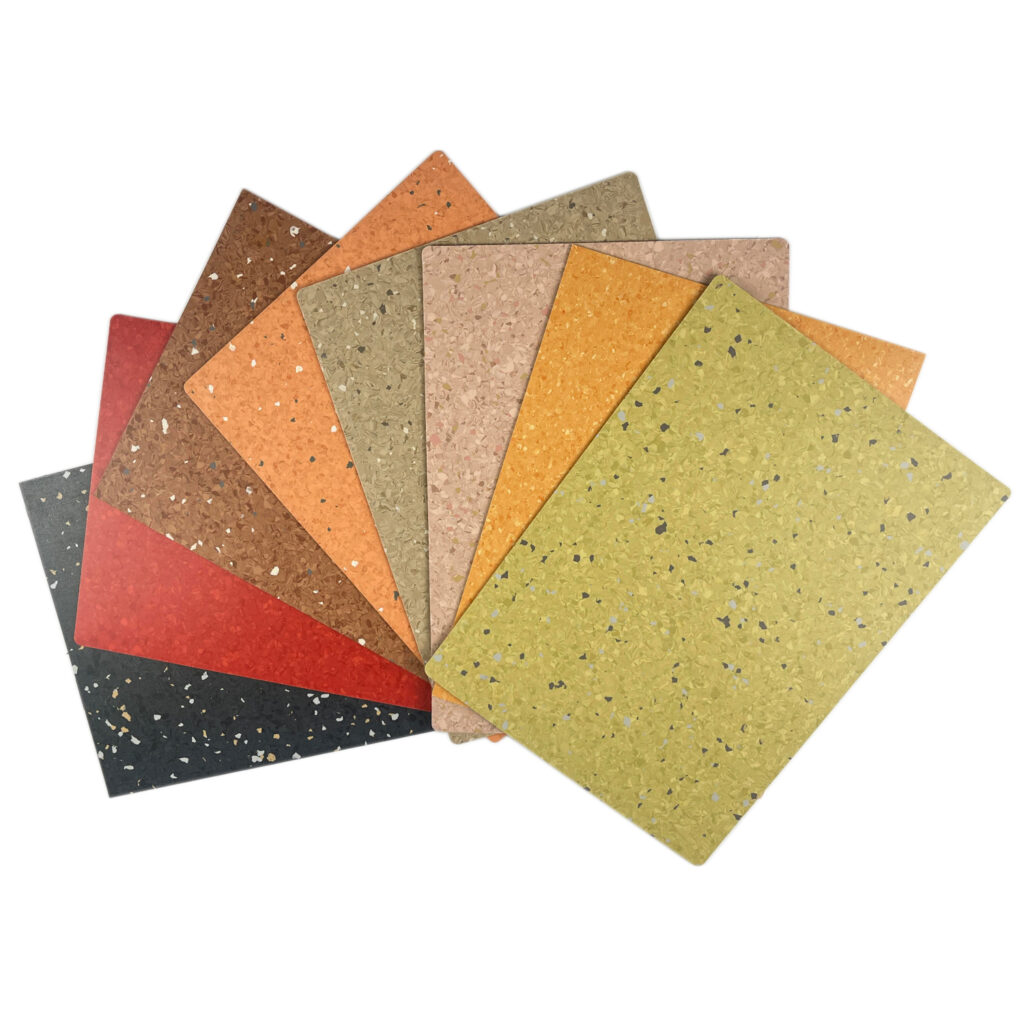
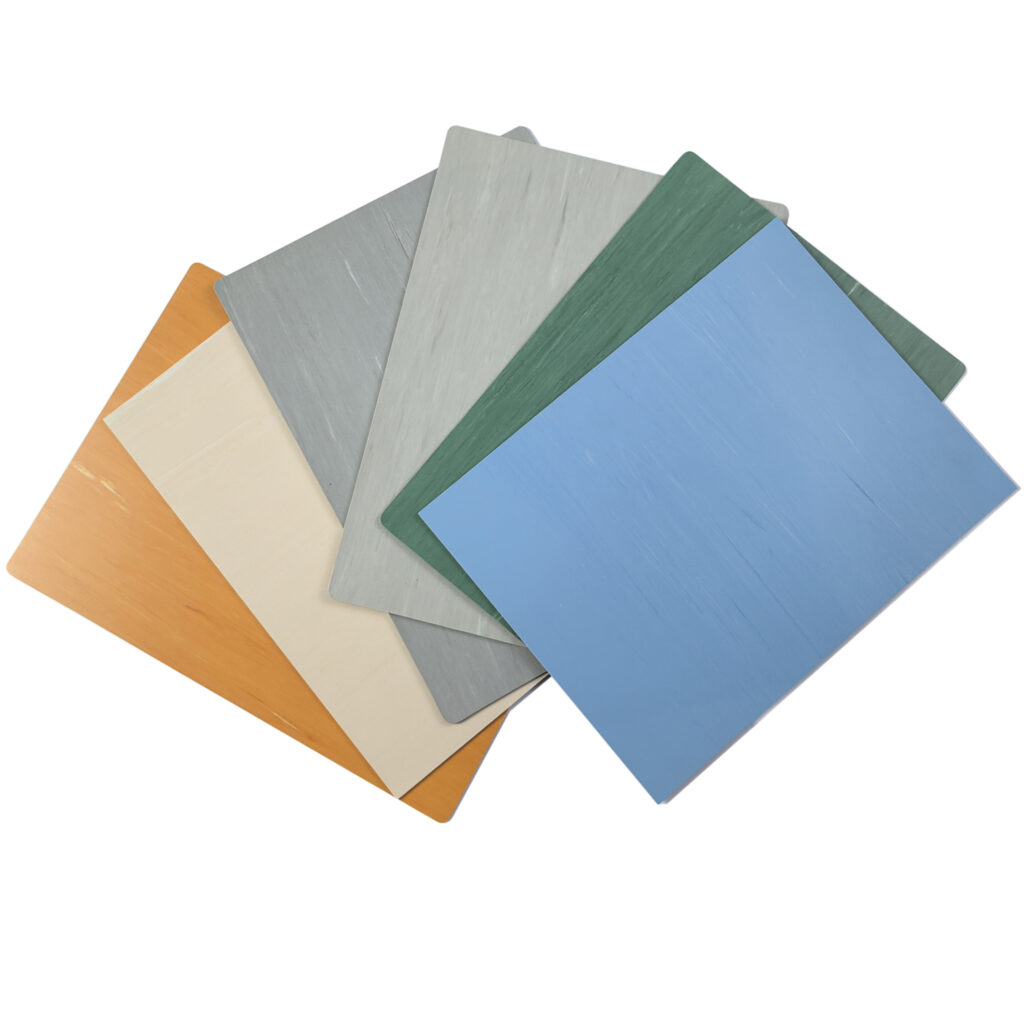


2. Wear Resistance & Durability
Non-directional: Typically offers higher wear resistance (Grade P or T), making it ideal for high-traffic environments and ensuring a longer lifespan.
Directional: Usually provides standard wear resistance (Grade P or below), suitable for areas with lower foot traffic.
3. Weight & Performance
Non-directional: Lighter in weight (approx. 2800–3000g/m² for 2mm thickness) but engineered for better strength and performance.
Directional: Heavier (around 3200g/m² for 2mm), yet overall performance may not match that of non-directional types.
4. Applications
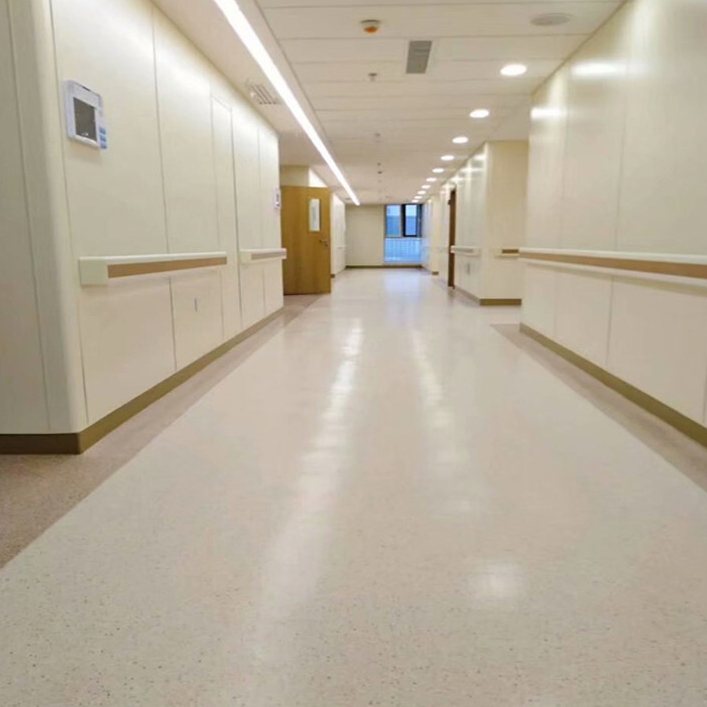
Non-directional: Preferred in hospitals, schools, offices, and other public facilities due to superior durability and ease of maintenance.
Directional: More suitable for light-use areas where cost is a concern and design alignment can be controlled.

5. Cost
Directional flooring is generally more economical and offers a budget-friendly solution.
Non-directional flooring, while more expensive, provides better long-term value due to enhanced durability and performance.